Distributed Database¶
Feng Li¶
Central University of Finance and Economics¶
feng.li@cufe.edu.cn¶
Course home page: https://feng.li/distcomp¶
Why Hive?¶
Many of those low-level details are actually quite repetitive from one job to the next, from low-level chores like wiring together Mappers and Reducers to certain data manipulation constructs, like filtering for just the data you want and performing SQL-like joins on data sets.
Hive not only provides a familiar programming model for people who know SQL, it also eliminates lots of boilerplate and sometimes-tricky coding you would have to do in Hadoop.
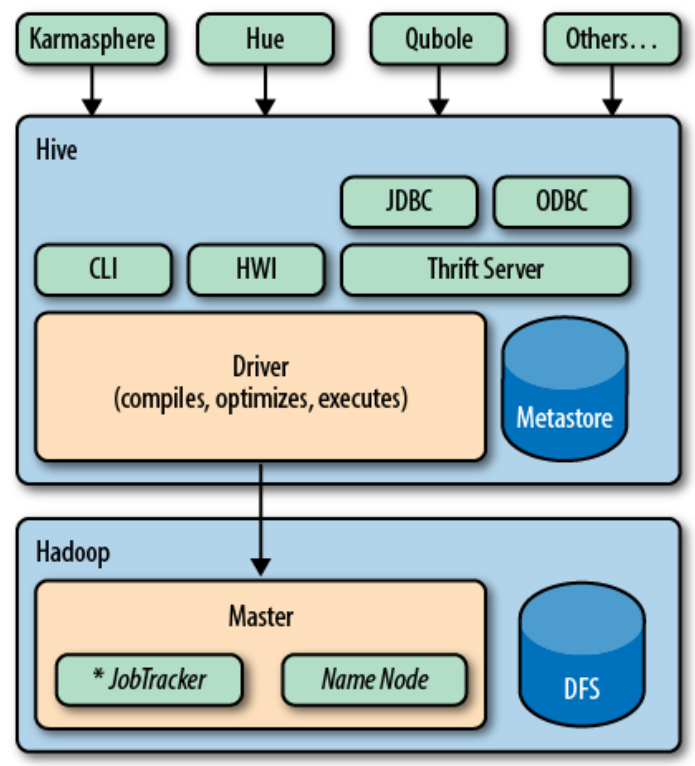
How does Hive work?¶
When MapReduce jobs are required, Hive doesn't generate Java MapReduce programs.
Instead, it uses built-in, generic Mapper and Reducer modules that are driven by an XML file representing the job plan
In other words, these generic modules function like mini language interpreters and the language to drive the computation is encoded in XML.
Hive Batch (old API)¶
Run hive commands from the termial
$ hive -e "dfs -ls /;"
Run Hive scripts from the termimal
$ hive -f /path/to/file/withqueries.hql
Hive Interactive (old API)¶
Start Hive from a Terminal
$ hive
Execute command within Hive
hive> dfs -ls /;
Exit Hive
hive> exit;
Beeline client with HiveServer2 (new interactive API)¶
Beeline is a Hive client for running Hive query and it also works with HiveQL file.
Beeline uses JDBC to connect to HiveServer2.
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://$HIVESERVER2_HOST:$HIVESERVER2_PORTFor a recent hive server, the address and port could be
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master:10000
Beeline client (batch mode)¶
Beeline executes an query
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master:10000 -e 'dfs -ls /;'Beeline executes a script.
beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master:10000 -f test.hql
dfs -ls /;
| DFS Output | |
|---|---|
| 0 | Found 7 items |
| 1 | drwxr-x--x - hadoop hadoop 0 201... |
| 2 | drwxrwxrwx - flowagent hadoop 0 201... |
| 3 | drwxr-x--x - student hadoop 0 201... |
| 4 | drwxr-x--x - hadoop hadoop 0 201... |
| 5 | drwxrwxrwx - root hadoop 0 201... |
| 6 | drwxr-x--t - hadoop hadoop 0 201... |
| 7 | -rw-r----- 2 student hadoop 19904316 201... |
Hive with Database¶
- Show Databases
SHOW DATABASES;
| database_name | |
|---|---|
| 0 | default |
| 1 | mydb |
SHOW DATABASES Like 'd*';
| database_name | |
|---|---|
| 0 | default |
- Create a Database
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS mydb;
Table created!
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS financials LOCATION '/user/lifeng/hive';
Table created!
SHOW DATABASES;
| database_name | |
|---|---|
| 0 | default |
| 1 | financials |
| 2 | mydb |
- Drop a database
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS financials;
SHOW DATABASES;
| database_name | |
|---|---|
| 0 | default |
| 1 | mydb |
- Use some database
USE mydb;
- Create a table within the database
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS mydb.employees (
name
STRING COMMENT 'Employee name',
salary
FLOAT COMMENT 'Employee salary',
subordinates ARRAY<STRING> COMMENT 'Names of subordinates',
deductions MAP<STRING, FLOAT>
COMMENT 'Keys are deductions names, values are percentages',
address
STRUCT<street:STRING, city:STRING, state:STRING, zip:INT>
COMMENT 'Home address')
COMMENT 'Description of the table'
TBLPROPERTIES ('creator'='me', 'created_at'='2012-01-02 10:00:00');
Table created!
SHOW TABLES;
| tab_name | |
|---|---|
| 0 | employees |
- Create an external table
Assume we have a data file stocks.txt located in HDFS at /user/lifeng/data, we could connect it with Hive as an external table.
create external table if not exists stocks (
symbol string,
ymd string,
price_open float,
price_high float,
price_low float,
price_close float,
volume int,
price_adj_close float )
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
location '/user/lifeng/data';
Table created!
If you have an external file with a header/footer, you could exclude it with
TBLPROPERTIES('skip.header.line.count'='1', 'skip.footer.line.count'='2');
when you create the table.
- Basic Statistics with Hive
SELECT avg(price_close) FROM stocks WHERE symbol = 'AAPL';
| _c0 | |
|---|---|
| 0 | 69.363 |
Alternatives to Hive¶
Pig¶
Suppose you have one or more sources of input data and you need to perform a complex set of transformations to generate one or more collections of output data.
Pig is described as a data flow language, rather than a query language. In Pig, you write a series of declarative statements that define relations from other relations, where each new relation performs some new data transformation. Pig looks at these declarations and then builds up a sequence of MapReduce jobs to perform the transformations until the final results are computed the way that you want.
A drawback of Pig is that it uses a custom language not based on SQL.
See th Pig home page https://pig.apache.org/ for more information.
HBase¶
HBase is inspired by Google’s Big Table.
It provides distributed and scalable data store that supports row-level updates, rapid queries, and row-level transactions (but not multirow transactions)
HBase uses HDFS for durable file storage of data.
HBase also uses in-memory caching of data.
HBase doesn’t provide a query language like SQL, but Hive is now integrated with HBase.
See the HBase homepage https://hbase.apache.org/ for more information.
Lab¶
Create an external table with Hive for the data
airdelay_small.csvorused_cars_data_small.csvUse the Hive internal functions to do basic statistic as we had with Hadoop.
External Reading¶
Capriolo, Edward, Dean Wampler, and Jason Rutherglen. Programming Hive: Data warehouse and query language for Hadoop. ” O’Reilly Media, Inc.”, 2012.