Introduction to Hadoop¶
Feng Li¶
Central University of Finance and Economics¶
feng.li@cufe.edu.cn¶
Course home page: https://feng.li/distcomp¶
What is Hadoop?¶
Hadoop is a platform that provides both distributed storage and computational capabilities.
Hadoop is a distributed master-worker architecture consists of the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) for storage and MapReduce for computational capabilities.
A Brief History of Hadoop¶
Hadoop was created by Doug Cutting.
At the time Google had published papers that described its novel distributed filesystem, the Google File System ( GFS ), and MapReduce, a computational framework for parallel processing.
The successful implementation of these papers’ concepts resulted in the Hadoop project.
Who use Hadoop?
- Facebook uses Hadoop, Hive, and HB ase for data warehousing and real-time application serving.
- Twitter uses Hadoop, Pig, and HB ase for data analysis, visualization, social graph analysis, and machine learning.
- Yahoo! uses Hadoop for data analytics, machine learning, search ranking, email antispam, ad optimization...
- eBay, Samsung, Rackspace, J.P. Morgan, Groupon, LinkedIn, AOL , Last.fm...
But we (statisticians, financial analysts) are not yet there!
--- and we should!
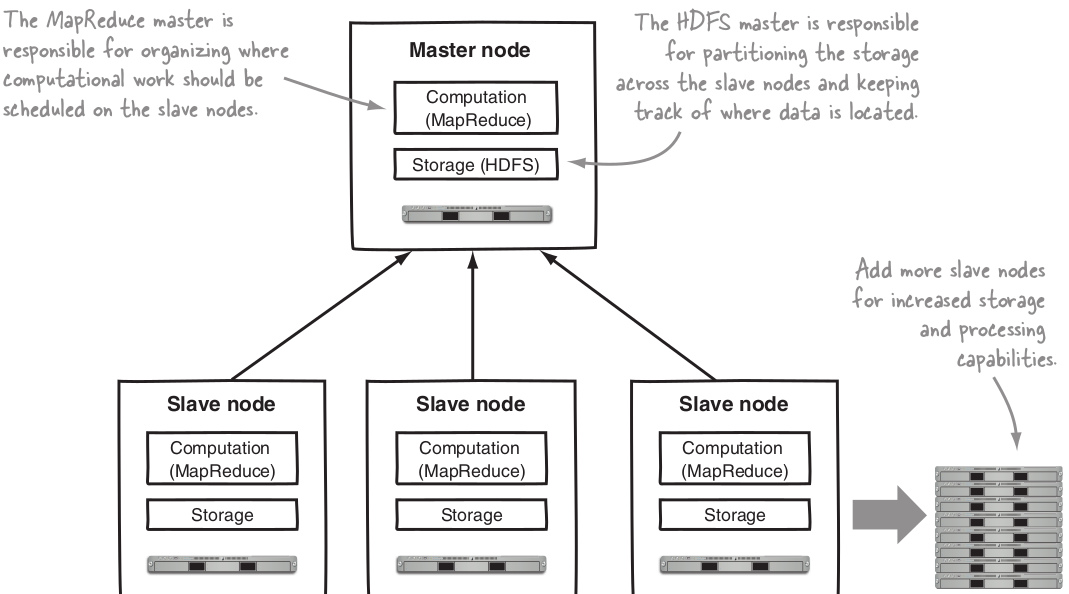
Core Hadoop components: HDFS¶
HDFS is the storage component of Hadoop
It’s a distributed file system.
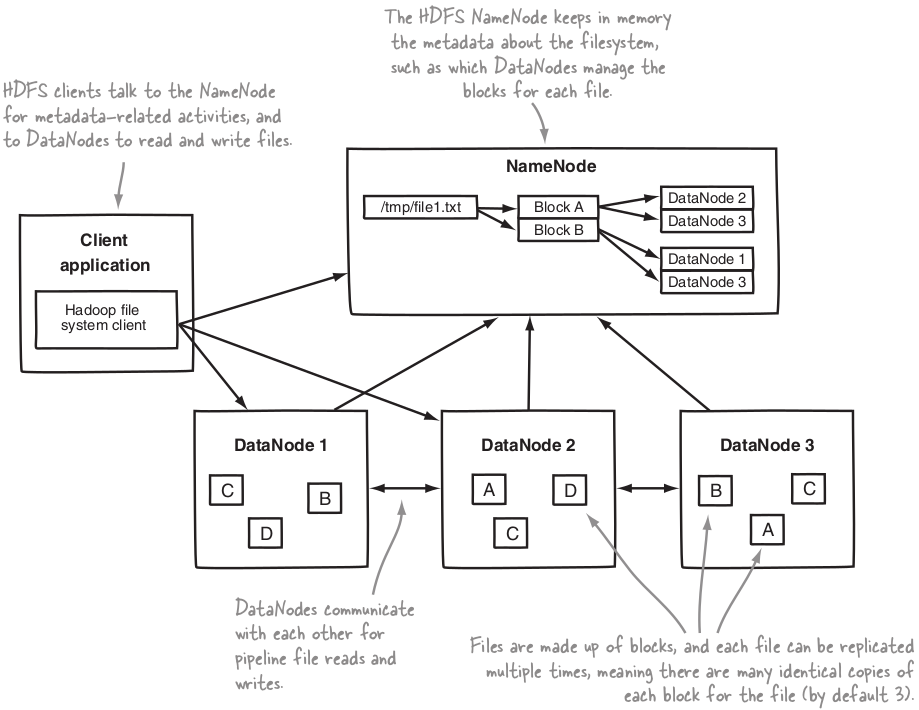
Logical representation of the components in HDFS : the NameNode and the DataNode.
HDFS replicates files for a configured number of times, is tolerant of both software and hardware failure, and automatically re-replicates data blocks on nodes that have failed.
HDFS isn’t designed to work well with random reads over small files due to its optimization for sustained throughput.
Core Hadoop components: MapReduce¶
- MapReduce is a batch-based, distributed computing framework.
- It allows you to parallelize work over a large amount of raw data.
- This type of work, which could take days or longer using conventional serial programming techniques, can be reduced down to minutes using MapReduce on a Hadoop cluster.
- MapReduce allows the programmer to focus on addressing business needs, rather than getting tangled up in distributed system complications.
- MapReduce doesn’t lend itself to use cases that need real-time data access.
The building blocks of Hadoop¶
- NameNode
- DataNode
- Secondary NameNode
- JobTracker
- TaskTracker
NameNode¶
The NameNode is the master of HDFS that directs the worker DataNode daemons to perform the low-level I/O tasks.
The NameNode keeps track of how your fi les are broken down into fi le blocks, which nodes store those blocks, and the overall health of the distributed file system.
The NameNode is a single point of failure of your Hadoop cluster
Secondary NameNode¶
An assistant daemon for monitoring the state of the cluster HDFS.
Each cluster has one Secondary NameNode.
The secondary NameNode snapshots help minimize the downtime and loss of data due to the failure of NameNode
DataNode¶
Each worker machine in your cluster will host a DataNode daemon to perform the grunt work of the distributed file system -- reading and writing HDFS blocks to actual files on the local file system.
DataNodes are constantly reporting to the NameNode.
Each of the DataNodes informs the NameNode of the blocks it’s currently storing. After this mapping is complete, the DataNodes continually poll the NameNode to provide information regarding local changes as well as receive instructions to create, move, or delete blocks from the local disk.
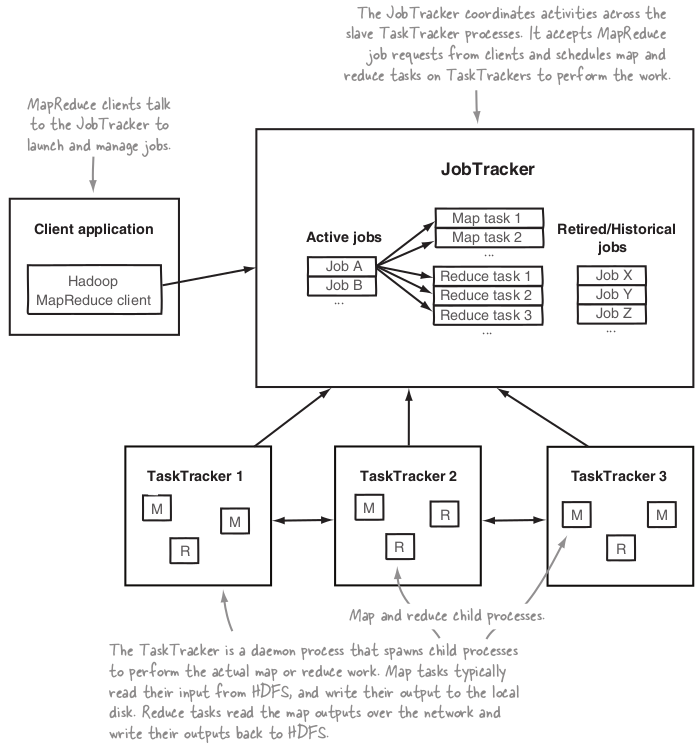
JobTracker¶
There is only one JobTracker daemon per Hadoop cluster. It’s typically run on a server as a master node of the cluster.
The JobTracker determines the execution plan by determining which fi les to process, assigns nodes to different tasks, and monitors all tasks as they’re running. Should a task fail, the JobTracker will automatically relaunch the task, possibly on a different node, up to a predefi ned limit of retries.
TaskTracker¶
Each TaskTracker is responsible for executing the individual tasks that the JobTracker assigns.
If the JobTracker fails to receive a heartbeat from a TaskTracker within a specified amount of time, it will assume the TaskTracker has crashed and will resubmit the corresponding tasks to other nodes in the cluster.
Setting up Hadoop¶
Basic requirements
- Linux machines (master 1, workers >= two)
- SSH (with passless login)
- Setup environment variables:
JAVA_HOME,HADOOP_HOME
Cluster setup: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/ClusterSetup.html
Core Hadoop configuration files
core-site.xmlmapred-site.xmlhdfs-site.xml
Demo Hadoop config at https://github.com/feng-li/hadoop-spark-conf
Work with Hadoop File System¶
hadoop
Usage: hadoop [--config confdir] [COMMAND | CLASSNAME]
CLASSNAME run the class named CLASSNAME
or
where COMMAND is one of:
fs run a generic filesystem user client
version print the version
jar <jar> run a jar file
note: please use "yarn jar" to launch
YARN applications, not this command.
checknative [-a|-h] check native hadoop and compression libraries availability
distcp <srcurl> <desturl> copy file or directories recursively
archive -archiveName NAME -p <parent path> <src>* <dest> create a hadoop archive
classpath prints the class path needed to get the
credential interact with credential providers
Hadoop jar and the required libraries
daemonlog get/set the log level for each daemon
trace view and modify Hadoop tracing settings
Most commands print help when invoked w/o parameters.
hadoop version
Hadoop 2.7.2 Subversion git@gitlab.alibaba-inc.com:soe/emr-hadoop.git -r 01979868624477e85d8958501eb27a460ce81e4c Compiled by root on 2018-08-31T09:14Z Compiled with protoc 2.5.0 From source with checksum 4447ed9f24dcd981df7daaadd5bafc0 This command was run using /opt/apps/ecm/service/hadoop/2.7.2-1.3.1/package/hadoop-2.7.2-1.3.1/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-common-2.7.2.jar
echo $JAVA_HOME
/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0
echo $HADOOP_HOME
/usr/lib/hadoop-current
echo $HADOOP_CLASSPATH
/usr/lib/hadoop-current/lib/*:/usr/lib/tez-current/*:/usr/lib/tez-current/lib/*:/etc/ecm/tez-conf:/usr/lib/hadoop-current/lib/*:/usr/lib/tez-current/*:/usr/lib/tez-current/lib/*:/etc/ecm/tez-conf:/opt/apps/extra-jars/*:/usr/lib/spark-current/yarn/spark-2.4.4-yarn-shuffle.jar:/opt/apps/extra-jars/*:/usr/lib/spark-current/yarn/spark-2.4.4-yarn-shuffle.jar
echo $HADOOP_CONF_DIR
/etc/ecm/hadoop-conf
hadoop fs
Usage: hadoop fs [generic options]
[-appendToFile <localsrc> ... <dst>]
[-cat [-ignoreCrc] <src> ...]
[-checksum <src> ...]
[-chgrp [-R] GROUP PATH...]
[-chmod [-R] <MODE[,MODE]... | OCTALMODE> PATH...]
[-chown [-R] [OWNER][:[GROUP]] PATH...]
[-copyFromLocal [-f] [-p] [-l] <localsrc> ... <dst>]
[-copyToLocal [-p] [-ignoreCrc] [-crc] <src> ... <localdst>]
[-count [-q] [-h] <path> ...]
[-cp [-f] [-p | -p[topax]] <src> ... <dst>]
[-createSnapshot <snapshotDir> [<snapshotName>]]
[-deleteSnapshot <snapshotDir> <snapshotName>]
[-df [-h] [<path> ...]]
[-du [-s] [-h] <path> ...]
[-expunge]
[-find <path> ... <expression> ...]
[-get [-p] [-ignoreCrc] [-crc] <src> ... <localdst>]
[-getfacl [-R] <path>]
[-getfattr [-R] {-n name | -d} [-e en] <path>]
[-getmerge [-nl] <src> <localdst>]
[-help [cmd ...]]
[-ls [-d] [-h] [-R] [<path> ...]]
[-mkdir [-p] <path> ...]
[-moveFromLocal <localsrc> ... <dst>]
[-moveToLocal <src> <localdst>]
[-mv <src> ... <dst>]
[-put [-f] [-p] [-l] <localsrc> ... <dst>]
[-renameSnapshot <snapshotDir> <oldName> <newName>]
[-rm [-f] [-r|-R] [-skipTrash] <src> ...]
[-rmdir [--ignore-fail-on-non-empty] <dir> ...]
[-setfacl [-R] [{-b|-k} {-m|-x <acl_spec>} <path>]|[--set <acl_spec> <path>]]
[-setfattr {-n name [-v value] | -x name} <path>]
[-setrep [-R] [-w] <rep> <path> ...]
[-stat [format] <path> ...]
[-tail [-f] <file>]
[-test -[defsz] <path>]
[-text [-ignoreCrc] <src> ...]
[-touchz <path> ...]
[-truncate [-w] <length> <path> ...]
[-usage [cmd ...]]
Generic options supported are
-conf <configuration file> specify an application configuration file
-D <property=value> use value for given property
-fs <local|namenode:port> specify a namenode
-jt <local|resourcemanager:port> specify a ResourceManager
-files <comma separated list of files> specify comma separated files to be copied to the map reduce cluster
-libjars <comma separated list of jars> specify comma separated jar files to include in the classpath.
-archives <comma separated list of archives> specify comma separated archives to be unarchived on the compute machines.
The general command line syntax is
bin/hadoop command [genericOptions] [commandOptions]
hadoop fs -ls /
Found 6 items drwxr-x--x - hadoop hadoop 0 2020-01-06 13:27 /apps drwxr-x--x - lifeng hadoop 0 2020-02-20 10:54 /data drwxrwxrwx - flowagent hadoop 0 2020-01-06 13:27 /emr-flow drwxr-x--x - hadoop hadoop 0 2020-02-10 22:20 /spark-history drwxrwxrwx - root hadoop 0 2020-02-26 21:36 /tmp drwxr-x--t - hadoop hadoop 0 2020-02-22 15:56 /user
hadoop fs -ls /user
Found 4 items drwx------ - hadoop hadoop 0 2020-01-06 13:29 /user/hadoop drwxr-x--x - hadoop hadoop 0 2020-01-06 13:27 /user/hive drwxr-x--x - lifeng hadoop 0 2020-02-21 12:06 /user/lifeng drwx------ - student hadoop 0 2020-02-22 15:28 /user/student
hadoop fs -put /opt/apps/ecm/service/hive/2.3.3-1.0.2/package/apache-hive-2.3.3-1.0.2-bin/binary-package-licenses/asm-LICENSE .
hadoop fs -ls /user/lifeng
Found 2 items drwxr-x--x - lifeng hadoop 0 2020-02-10 22:20 /user/lifeng/.sparkStaging -rw-r----- 2 lifeng hadoop 1511 2020-02-26 21:36 /user/lifeng/asm-LICENSE
hadoop fs -mv asm-LICENSE license.txt