Introduction to Spark¶
Feng Li¶
Guanghua School of Management¶
Peking University¶
feng.li@gsm.pku.edu.cn¶
Course home page: https://feng.li/bdcf¶
What is Spark¶
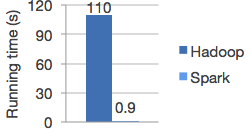
Spark is the big data distributed computing version of TensorFlow/PyTorch for deep learning.
Programming & Usability¶
| Feature | Apache Spark | TensorFlow/PyTorch |
|---|---|---|
| Languages Supported | Scala, Java, Python, R | Python (main), C++, Java (limited) |
| Ease of Use | High-level APIs (DataFrame, SQL) | PyTorch: Easier for research; TensorFlow: More optimized for production |
| Learning Curve | Moderate (requires understanding of distributed computing) | PyTorch: Easier; TensorFlow: Steeper curve (especially older versions) |
Scalability & Performance¶
| Feature | Apache Spark | TensorFlow/PyTorch |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Scales horizontally (across clusters) | Scales vertically (leveraging multiple GPUs/TPUs) |
| Distributed Computing | Yes (native support for cluster computing) | Requires additional tools like Horovod or PyTorch Distributed |
| Speed | Optimized for large-scale distributed data processing | Optimized for numerical operations and matrix multiplications |
Machine Learning Support¶
| Feature | Apache Spark | TensorFlow/PyTorch |
|---|---|---|
| Built-in ML | Yes (MLlib, MLFlow integration) | No (but specialized for deep learning) |
| Deep Learning Support | Limited (via TensorFlowOnSpark, Deep Learning Pipelines) | Specialized for neural networks, CNNs, RNNs, transformers, etc. |
Who created Spark¶
Spark was a PhD student project in Berkerley University.
Matei Zaharia was the major contributor during his PhD at UC Berkeley in 2009.
Matei’s research work was recognized through the 2014 ACM Doctoral Dissertation Award for the best PhD dissertation in computer science, an NSF CAREER Award, and the US Presidential Early Career Award for Scientists and Engineers (PECASE).
Ease of Use¶
Write applications quickly in Java, Scala, Python, R, and SQL.
Spark offers over 80 high-level operators that make it easy to build parallel apps. And you can use it interactively from the Scala, Python, R, and SQL shells.
DataFrame with pandas API support
Generality¶
Combine SQL, streaming, and complex analytics.
Spark powers a stack of libraries including SQL and DataFrames, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX, and Spark Streaming. You can combine these libraries seamlessly in the same application.
Runs Everywhere¶
Spark runs on Hadoop, Apache Mesos, Kubernetes, standalone, or in the cloud. It can access diverse data sources.
You can run Spark using its standalone cluster mode, on EC2, on Hadoop YARN, on Mesos, or on Kubernetes. Access data in HDFS, Alluxio, Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, Apache Hive, and hundreds of other data sources.

Spark architecture¶

Spark Built-in Libraries:¶
- SQL and DataFrames
- Spark Streaming
- MLlib, ML (machine learning)
- GraphX (graph)
Run a Python application on a Spark cluster¶
PYSPARK_PYTHON=python3.12 spark-submit \
--master https:1.2.3.4 \
examples/src/main/python/pi.py \
1000
Interactively Run Spark via Pyspark¶
It is also possible to launch the PySpark shell. Set
PYSPARK_PYTHONvariable to select the approperate Python when runningpysparkcommand:PYSPARK_PYTHON=python3.12 pyspark
Run Spark interactively within Jupyter Notebook¶
You could use Spark as a Python module
On PKU HPC, you could access it by create your own notebook at
Then you could import the
pysparkmodule
Install Python modules on PKU HPC¶
The running nodes (the Jupyter Notebook) do not have internet access
One has to install everything from the login node using proper version of Python pip
In the Jupyter, use
os.path.dirname(sys.executable)to allocate the path for pip. It returns something like/nfs-share/software/anaconda/2020.02/envs/python3.12/binIn the login node, run like
/nfs-share/software/anaconda/2020.02/envs/python3.12/bin/pip install statsmodels
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Initialize a Spark session
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.config("spark.ui.enabled", "false") \
.appName("MyPySparkApp") \
.getOrCreate()
# Check if Spark is running
print(spark.version)
Setting default log level to "WARN". To adjust logging level use sc.setLogLevel(newLevel). For SparkR, use setLogLevel(newLevel). 25/02/23 21:40:35 WARN NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
3.5.4
spark
SparkSession - in-memory
Stop a Spark session¶
spark.stop()